In the ever-evolving world of digital design, understanding the distinction between User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI) design is crucial for both professionals and businesses. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent fundamentally different aspects of the design process that work together to create successful digital products.
What is UX Design?
User Experience (UX) design focuses on the overall experience a user has when interacting with a product or service. It encompasses all aspects of the end-user’s interaction with the company, its services, and its products. UX designers are concerned with the entire journey of user interaction, from initial contact to final engagement.

Key Components of UX Design
- User Research and Analysis
- Conducting user interviews and surveys
- Creating user personas
- Analyzing user behavior patterns
- Identifying pain points and opportunities
- Information Architecture
- Organizing content structure
- Creating user flows
- Developing site maps
- Planning navigation systems
- Wireframing and Prototyping
- Creating low-fidelity mockups
- Developing interactive prototypes
- Testing user flows
- Iterating based on feedback
What is UI Design?
User Interface (UI) design focuses on the visual and interactive elements of a digital product. It’s the point of interaction between users and digital devices or applications. UI designers are responsible for creating visually appealing and intuitive interfaces that users can easily navigate.

Core Elements of UI Design
- Visual Design
- Color schemes and typography
- Button styles and icons
- Layout and spacing
- Visual hierarchy
- Interactive Elements
- Animations and transitions
- Responsive design
- Micro-interactions
- Visual feedback
Key Differences Between UX and UI Design
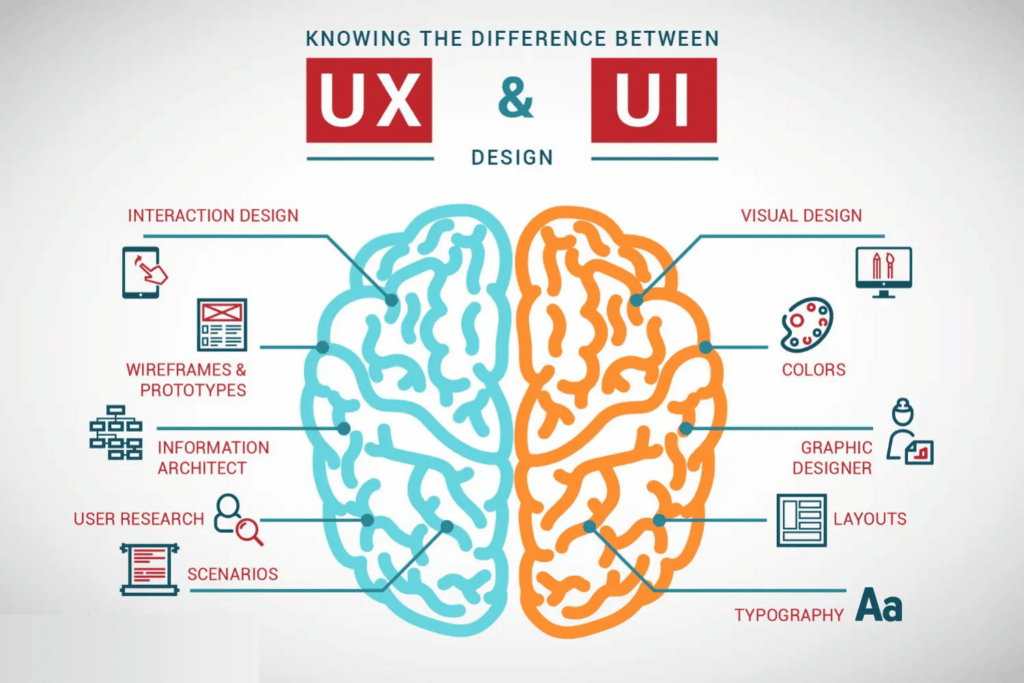
1. Scope and Focus
UX Design:
- Focuses on the overall user journey
- Involves strategic planning and research
- Considers all aspects of user interaction
- Applies to both digital and physical products
UI Design:
- Concentrates on visual interface elements
- Focuses on aesthetic appeal and functionality
- Deals specifically with digital interfaces
- Emphasizes visual consistency and brand alignment
2. Process and Methodology
UX Design Process:
- User research and analysis
- Creating user personas
- Developing wireframes
- Conducting usability testing
- Iterating based on feedback
UI Design Process:
- Creating visual style guides
- Designing interface elements
- Developing high-fidelity mockups
- Ensuring visual consistency
- Implementing interactive elements
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Airbnb’s Design Evolution
Airbnb’s success demonstrates the perfect harmony between UX and UI design. The UX team focused on improving user trust and streamlining the booking process, while the UI team ensured visual consistency and usability across platforms.
Spotify’s User-Centric Approach
Spotify’s design showcases how UX and UI work together. The UX design focuses on personalization and user engagement through features like “Discover Weekly,” while the UI design maintains a clean and intuitive interface across devices.
Tools and Software for UX and UI Design
Popular UX Design Tools
- Figma: Excellent for collaborative UX design and prototyping
- Adobe XD: Comprehensive tool for wireframing and prototyping
- UXPin: Specialized in design systems and prototyping
Popular UI Design Tools
- Sketch: Preferred by UI designers for interface design
- InVision Studio: Strong capabilities for interactive designs
- Zeplin: Bridges the gap between design and development
Best Practices for Both Disciplines
UX Design Best Practices
- User-Centric Approach: Always design with the end-user in mind
- Iterative Design: Continuously test and refine based on user feedback
- Accessibility: Ensure designs are usable by everyone
UI Design Best Practices
- Consistency: Maintain visual consistency across all interface elements
- Simplicity: Create clean, uncluttered interfaces
- Feedback: Provide clear visual feedback for user actions
Conclusion
While UX and UI design serve different purposes, they are complementary disciplines that work together to create successful digital products. Understanding these differences is crucial for creating products that are not only visually appealing but also provide an excellent user experience. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the importance of both UX and UI design in creating successful digital products cannot be overstated.